What exactly is intelligence?
Intelligence is the ability of living beings to understand, learn, solve problems and adapt to their environment. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a computer science discipline that aims to reproduce these capabilities in machines. It aims to develop systems capable of reasoning, learning, perceiving and interacting autonomously, similar to a human being.
AI can be classified into several models, including computational AI, biological AI and hybrid AI.
Computational AI relies on algorithms and data processing techniques to simulate human intelligence. For example, it draws on the processes and structures of the brain and nervous system to create intelligent systems.
Biological AI is inspired by living organisms and attempts to use nature to create an intelligent solution (cells, living organisms, cloning).
Hybrid AI combines both approaches.
30 important dates in the history of artificial intelligence:
1. 1943: Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts propose the artificial neuron model.

2. 1950: Alan Turing proposes the “Turing Test” to evaluate machine intelligence.
3. 1956: The Dartmouth Conference marks the official start of AI as a field of research.
4. 1956: John McCarthy invents the LISP programming language, used in AI.
6. 1965: Joseph Weizenbaum creates ELIZA, a natural language processing program.
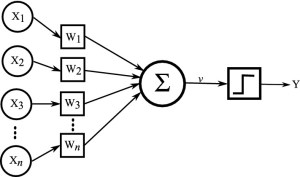
5. 1958: Frank Rosenblatt develops the perceptron, an artificial neural network model.

7. 1969: Shakey, the first autonomous mobile robot, is developed at Stanford University.
8. 1973: James Lighthill publishes a report criticizing the progress of AI, triggering an “AI winter”.
9. 1980: Expert systems become increasingly popular in industrial applications.
10. 1986: Geoffrey Hinton and colleagues introduce the deep neural network model.
11. 1986 Marvin Minsky publishes the book “The Society og Mind” (theory of elementary autonomous and organized agents).

1997 Deep Blue, an IBM supercomputer, defeats world chess champion Garry Kasparov.
12. 2000: The Python programming language becomes popular for AI development.
13. 2006: Andrew Ng and his team develop deep learning models for object recognition.

14. 2011: IBM Watson wins the Jeopardy! game show using natural language processing techniques.
15. 2012: AI reaches a milestone with AlexNet’s (by Alex Krizhevsky) convolutional neural network for computer vision.
16. 2014: Google develops AI by acquiring DeepMind (Demis Hassabis, Mustafa Suleyman (en) and Shane Legg), which beats the world champions at the game of Go.

17. 2016: AI-powered chatbots become popular for simulated human interactions.
18. 2017: AlphaGo Zero, an improved version of DeepMind’s AI, learns to play go without any human input.
19. 2018: OpenAI develops the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) AI for text generation.
20. 2019 : Autonomous vehicles begin to be tested on public roads in some countries.
21. 2020 : AI is used in drug discovery and disease spread modeling, notably during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The connections versus the symbolic approach
The connectionist approach, also known as deep learning, focuses on artificial neural networks and data-driven learning. Researchers such as Geoffrey Hinton, Yann LeCun and Yoshua Bengio have played a major role in the development of this approach. It is based on the simulation of human learning using interconnected artificial neural networks.
The symbolic approach, on the other hand, relies on the manipulation of symbols and logical rules to simulate human reasoning. Researchers such as Allen Newell, John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky have been key figures in this approach. It focuses on the creation of systems based on symbolic representations and rules for manipulating these symbols.
The 20 main concepts and models in AI :
1. Expert systems – Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon
2. Blackboard – Edward Feigenbaum
3. Intelligent agents – Rodney Brooks
4. Neural networks – Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts
5. Deep Learning – Geoffrey Hinton, Yann LeCun, Yoshua Bengio
6. Machine Learning – Arthur Samuel, Tom Mitchell
7. Natural Language Processing (NLP) – Karen Sparck Jones
8. Computer vision – David Marr
9. Robotics – Rodney Brooks, Cynthia Breazeal
10. Generative Antagonistic Networks (GAN) – Ian Goodfellow
11. generative AI – Jürgen Schmidhuber
12. Fuzzy logic – Lotfi A. Zadeh
13. Multi-agent systems – Michael Wooldridge
14. Evolutionary AI – John R. Koza
15. Reinforcement learning – Richard S. Sutton, Andrew Barto
16. Deductive logic – Alonzo Church
17. Recommender systems – Joseph Konstan, John Riedl
18. Emotional AI – Rosalind Picard
19. Probabilistic reasoning – Judea Pearl
20. symbolic AI – Marvin Minsky, John McCarthy
10 concepts inspired by and using living cells, molecules and biology for artificial intelligence:
1. DNA computation – Leonard Adleman
2. Bio-inspired computing – John Holland
3. Artificial neural networks – Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts
4. Genetic algorithms – John Holland
5. Artificial neural networks spiking – Carver Mead
6. Particle swarm algorithm – Eberhart and Kennedy
7. Bio-inspired robotics – Rodney Brooks
8. Nanorobotics – Eric Drexler
9. Synthetic biology – Jay Keasling
10. Quantum computing – Peter Shor
10 research projects combining computational AI and biological/living systems
1. BrainGate – Development of brain-computer interfaces to help disabled people.
2. Human Brain Project – Research into human brain modeling and computational neuroscience.
3. Blue Brain Project – Digital brain mapping and simulation.
4. Optogenetics – Using genetic techniques to control neurons with light.
5. Robotic exoskeletons – Development of exoskeletons to augment human physical capabilities.
6. Biohybrid systems – Combining biological and artificial materials to create hybrid systems.
7. Synthetic biology – Engineering living cells to create specific functionalities.
8. DeepMind AI-assisted protein folding – Using AI to predict protein folding.
9. Optogenomics – Combining optogenetics and genomics to study neural circuits.
10. Bio-inspired robotics – Designing biologically-inspired robots for greater adaptability and resilience.
20 researchers who have made AI history
1. Alan Turing – Pioneer of computer science and AI, designer of the “Turing Test”.
2. John McCarthy – Inventor of the term “artificial intelligence” and co-founder of the field.
3. Marvin Minsky – Key figure in symbolic AI and expert systems.
4. Herbert A. Simon – Major contributor to expert systems and cognitive models.
5. Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts – Pioneers of artificial neural networks.
6. Joseph Weizenbaum – Creator of the natural language processing program ELIZA.
7. Rodney Brooks – Developer of autonomous robots and the intelligent agent approach.
8. Geoffrey Hinton, Yann LeCun, Yoshua Bengio – Leaders in deep learning and deep neural networks.
9. Ray Kurzweil – Pioneer of speech recognition systems and general artificial intelligence.
10. Jürgen Schmidhuber – Major contributor to neural networks and generative AI.
11. Judea Pearl – Expert in probabilistic reasoning and causality.
12. Cynthia Breazeal – Pioneer in social robotics and human-robot interaction.
13. Fei-Fei Li – Research in computer vision and ethical AI.
14. Andrew Ng – Machine learning expert and Coursera co-founder.
15. Demis Hassabis – Co-founder of DeepMind, specializing in general AI and gaming.
16. Karen Sparck Jones – Major contributions to natural language processing.
17. Sebastian Thrun – Co-founder of Google X and pioneer of autonomous driving.
18. Elon Musk – Visionary entrepreneur investing in AI and the future of technology.
19. Ian Goodfellow – Inventor of generative adversarial networks (GANs).
20. Yoshua Bengio – Major contributions to deep learning and neural networks.
20 current leaders in the field of AI and their respective contributions:
1. Ian Goodfellow – Inventor of generative adversarial networks (GANs).
2. Yoshua Bengio – Major contributions to deep learning and neural networks.
3. Geoffrey Hinton – Pioneer of deep learning and neural networks.
4. Andrew Ng – Machine learning expert, co-founder of Coursera.
5. Yann LeCun – Research on convolutional neural networks and natural language processing.
6. Fei-Fei Li – Research on computer vision and ethical AI.
7. Demis Hassabis – Co-founder of DeepMind, specializing in general AI and gaming.
8. MCynthia Breazeal – Pioneer of social robotics and human-robot interaction.
9. Karen Sparck Jones – Major contributions to natural language processing.
10. Sebastian Thrun – Expert in artificial intelligence and autonomous driving.
11. Elon Musk – Entrepreneur investing in AI with companies such as Neuralink and OpenAI.
12. Judea Pearl – Expert in probabilistic reasoning and causality.
13. Ray Kurzweil – Futurist and AI expert, specializing in future technologies.
14. Yoshua Bengio – Research into deep neural networks and deep learning.
15. Max Tegmark – AI expert and futurist, focusing on the social implications of AI.
16. Ian Goodfellow – Inventor of generative adversarial networks (GANs).
17. Rana el Kaliouby – Pioneer of emotional AI and human-machine interaction.
18. Pieter Abbeel – Expert in robotics and reinforcement learning.
19. Kate Crawford – Researcher in AI ethics and algorithmic justice.
20. Stuart Russell – AI expert, focusing on AI safety and ethics.
20 AI software solutions, organized by category:
1. Expert systems :
– IBM Watson (IBM) – AI platform that uses logical reasoning to solve complex problems.
2. Neural networks :
– TensorFlow (Google) – Open-source machine learning library based on neural networks.
– PyTorch (Facebook) – Development framework for deep learning based on neural networks.
3. Machine learning :
– scikit-learn – Open-source machine learning library for Python.
– Microsoft Azure ML – Cloud platform for developing and deploying machine learning models.
4. Natural language processing :
– Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) – Open-source natural language processing library for Python.
– SpaCy – Python library for advanced natural language processing and named entity recognition.
5. Computer vision :
– OpenCV – Open-source library for image processing and computer vision.
– TensorFlow Object Detection API (Google) – Machine learning tool for object detection in images.
6. Robotics :
– ROS (Robot Operating System) – Open-source platform for the development of robots and robotic systems.
– Robot Framework – Open-source test framework for developing and automating robotics tests.
7. generative AI :
– DeepArt (DeepArt.io) – Online tool using AI to generate works of art from photos.
– StyleGAN (NVIDIA) – Generative AI model for creating realistic images and videos.
8. Data analysis :
– Tableau Software – AI-based data analysis and visualization platform.
– Splunk – Real-time data analysis platform with AI and machine learning capabilities.
9. AI in healthcare :
– IBM Watson Health – AI platform for medical data analysis and clinical decision support.
– Butterfly iQ – Wearable ultrasound system using AI to improve image visualization and interpretation.
10. AI in finance :
– Quantopian – Investment platform based on AI and machine learning.
– Alpaca – AI-based trading platform with automation and data analysis tools.
6 unusual projects around AI and biology/hybrid solutions:
1. Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI): Using AI to enable people to control prostheses or electronic devices directly by thought.
2. Organ biofabrication: Using AI to model and 3D print living organs using cells and biomaterials.
3. Animal language translation systems: Using AI to understand and translate animal vocalizations and signals.
4. Hybrid Swarm Systems: Combining autonomous robots and live animals to perform complex tasks using collective intelligence.
5. Biologically-Inspired Neural Networks: Creation of artificial neural networks based on the structures and functions of biological neurons.
6. Medical Nanobots: Using nanobots to deliver drugs in a targeted way and perform minimal surgery.
The impact of AI in the next 20 years:
AI will have a signifiant impact in many areas over the next few years, so I’ve tried to pick out a few examples:
1. general issues: AI raises ethical, privacy and liability issues due to its autonomy and ability to make decisions without direct human intervention.
2. Education: AI can be used to personalize learning, provide tailored educational resources and help teachers assess students.
3. industry: AI will automate manufacturing processes, improve the quality and efficiency of operations, and facilitate predictive maintenance.
4. Banking: AI will enable more accurate risk analysis and management, improved fraud detection and more personalized banking services.
5. Digital: AI will be at the heart of the user experience, offering virtual assistants, personalized recommendations and more natural human-machine interfaces.
6. Metaverse: AI will play a crucial role in creating interactive and immersive virtual environments, powering augmented and virtual reality experiences.
7. Everyday life: AI will be ubiquitous, with intelligent assistants integrated into domestic appliances, cars, delivery services and more.
8. Marketing: AI will enable precise segmentation and personalization of marketing, improving the customer experience and the effectiveness of advertising campaigns.

Conclusion:
1. Biases in AI solutions can stem from biases embedded in training data. To avoid them, it is important to have diverse and representative datasets, as well as regular evaluation and correction of models.
2. The question of AI fear is a complex one. While there are legitimate concerns, responsible use, appropriate regulation and awareness can mitigate risks and enable significant benefits.
3. AI can help humans by increasing their capabilities, automating repetitive and dangerous tasks, improving healthcare and offering innovative solutions in various fields.
4. AI can help solve environmental problems by improving the modeling and management of natural resources, helping to find sustainable solutions and optimizing industrial processes to reduce environmental impact.
5. AI can draw inspiration from nature to create intelligent models and more resilient systems, using biological concepts and operating principles to solve complex problems.
6. AI has the potential to contribute to a better world by promoting equal opportunities, having a positive impact on society, encouraging responsibility and supporting environmentally-friendly practices.
However, vigilance and constant assessment of the social, ethical and environmental implications of AI are essential to ensure responsible deployment that benefits humanity.
Leave a comment